Identifying Posterior Calcaneal Spur
Overview
A heel spur is a hook of bone that can form on the heel bone of the foot. Heel spurs are associated with plantar fasciitis. Heel spurs can cause extreme pain in the rearfoot. The pain is most intense while standing or walking. What Causes Heel Spurs? Heel spurs develop as an abnormal growth in the heel bone due to calcium deposits that form when the plantar fascia stretches and pulls away from the heel. The plantar fascia is a ligament located at the bottom of your foot. This stretching of the plantar fascia is usually the result of flat feet or unusually high arches.
Causes
A heel spur usually develops as a result of wear and tear over time, which leads to the degeneration of connective tissue called fascia. Standing for prolonged periods and wearing shoes that do not provide the right type of arch support can also lead to connective tissue damage in the heel. The body attempts to repair the damaged tissue by delivering calcium to the affected region, but sometimes too much calcium begins to accumulate and this results in painful plantar fasciitis.
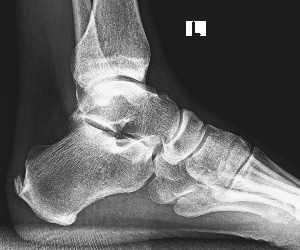
Symptoms
It is important to be aware that heel spurs may or may not cause symptoms. Symptoms are usually related to the plantar fasciitis. You may experience significant pain and it may be worse in the morning when you first wake up or during certain physical activities such as, walking, jogging, or running.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
Many treatment options exist, and good results are often observed. Generally, a calcaneal spur develops when proper care is not given to the foot and heels. It is often seen as a repetitive stress injury, and thus lifestyle modification is typically the basic course of management strategies. To alleviate heel spur pain, a person should begin doing foot and calf workouts. Strong muscles in the calves and lower legs will help take the stress off the bone and thus help cure or prevent heel spurs. Icing the area is an effective way to get immediate pain relief.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery involves releasing a part of the plantar fascia from its insertion in the heel bone, as well as removing the spur. Many times during the procedure, pinched nerves (neuromas), adding to the pain, are found and removed. Often, an inflamed sac of fluid call an accessory or adventitious bursa is found under the heel spur, and it is removed as well. Postoperative recovery is usually a slipper cast and minimal weight bearing for a period of 3-4 weeks. On some occasions, a removable short-leg walking boot is used or a below knee cast applied.
Prevention
If you have not yet developed this condition, you can take steps to protect yourself from it. Most importantly, make it a rule to wear properly fitted footwear. Avoid shoes that have become worn down in the heel, and don't choose shoes that cause you to walk in an abnormal fashion. Maintaining a healthy weight will ensure that undue pressure isn't being put on the ligaments, tendons and bones of your feet. If your job requires a great deal of time on your feet, or if you exercise regularly, be sure to balance periods of activity with periods of rest for your feet.